Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is costing which use to allocate overhead cost to each product based on activity consumption. This method will allocate cost to production activities, and each cost pool will be assigned to the product based on its consumption. It will link between the resource consumption with the output produce base on each activity. It assumes the activity will consume resources and will generate results. So we must calculate the cost per unit of all activity.
We usually use absorption costing for the traditional which does not reflect in real situations. In the modern way, we will use ABC that calculated based on cost drivers, the activities that increase the cost. While Absorption costing focuses on volume related to cost drivers.
Activity-Based Costing Process
- Identify the Process and Cost Pool: Cost pool is a group of individual cost such as service, department or stage of production. The first thing to do before applying ABC is to deeply understand the production process. How many stages does it take to convert the raw material to the finished product? Then we need to go through each stage to understand if one or two stages belong to the same cost pool. It is base on nature and judgment to combine multiple production stages into one ABC cost pool. These stages may consume the same cost or we are unable to separate the cost for each one.
- Identify the activity’s unit or cost driver: Cost driver is the factor that determine the total cost in each pool. Cost driver can be the number of set up, inspection hour and so on. It depends on the nature of production and its complexity. We have to balance between accuracy and difficulty in order to determine the cost driver. For example, the cost driver of the product set up stage can base on the unit or batch of production. It is more accurate to assign costs by each unit but how to get the actual data. If we use batch production, it will be like the absorption costing which we assume all products consume the same overhead.
- Allocate cost per unit of the driver: We simply take cost pool in step 1 and divide by the number of the cost driver in step 2.
- Allocate cost to each product: We simply take the cost per driver and divided by the number of units per driver. If an individual unit is the cost driver, we do not need to allocate any more. At the end of this stage, we will know the cost per unit in each cost pool.
Activity-Based Costing Example
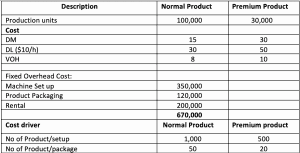
Step 1: identify cost pool
The cost pools are:
- Machine Set Up
- Product Packaging
- Rental
Based on example cost pools already identify, but in real life, we need to define base on the actual situation.
Step 2: Identify the cost driver
- Machine setup cost will drive by a number of set up time.
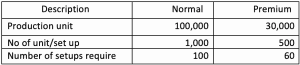
- Packaging costs will drive by a number of packaging.
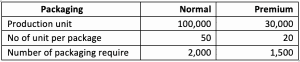
- The rental fee is the fixed cost which is not driven by any activities. It may base on Square meter or building rental which is hard to allocate. In this example, we will use the labor hour as the absorption method to allocate this cost.
| Normal | Premium | |
| Product | 100,000 | 30,000 |
| Direct Labor | 3 | 5 |
| Total direct labor require | 300,000 | 150,000 |
Step 3: These are the summary of costs per cost driver in each activity.
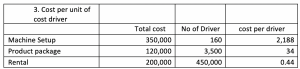
Step 4: Allocate overhead costs to both products:
| Normal | Premium | |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Material | 15 | 30 |
| Direct Labor | 30 | 50 |
| Variable Overhead | 8 | 10 |
| Machine Setup | 2.19 | 36.46 |
| Packaging | 0.68 | 0.022 |
| Rental | 1.33 | 2.22 |
| Total | 57.2 | 128.702 |
Benefits of Activity-Based Costing
| Benefits of Activities Base Costing | |
|---|---|
| More accurate on cost calculation | By using ABC, it will provide more accurate than other methods because it is deeply analyzing of cause and effect of each item in overhead costs. All costs are separated by the activities, and it will be transferred to the product which consume the activity. Cost will be included in each product only when it provides benefits to the product. |
| Help to reduce products’ costs by improving process | ABC helps to understand the nonvalue added activities that management needs to identify and eliminate. Moreover, the manager can improve important activities in order to cut the cost. |
| To get a better understanding of overhead cost | The manager will be able to understand the full picture of all overhead costs when all of the elements are broken down and analyze one by one. |
| Help management in setting proper prices | By taking into account all related costs, management will be able to set the competitive price in the market. |
| Effective resource allocation | ABC helps us to separate overhead into a cost pool with each cost driver, it will help management to understand production volume which will impact each cost pool. |
| Help to evaluate department performance | Help management to appraise each department by comparing the cost driver from time to time and investigate how it is fluctuated. |
How does ABC fit with current business?
Activity-Based Costing allows us to look into all product cost, profit and the benefit to customers. We can focus on the profitable products and increase its production to maximize the profit. On the other hand, the less profitable products may be decreased or outsource to the other companies that can produce better than us.
ABC also helps to improve our pricing strategy as well when all true costs have been included. Sometimes we may want to reduce the price to fight for market share, but we not sure what is the minimum price we can go. With ABC, every cost is included, so the management knows how much they can reduce the cost and its impact to the consumers.
Requirements for Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
The activity-based costing bases on the activity in the production and links it to the cost pool. A cost pool is a group of overhead cost which we are unable to allocate to each product. Matching cost pool and activity can be made by some assumptions.
The next step is to allocate each cost pool to the product by using cost drivers. We need to find a link between cost pool and each product. We have to understand how each product consume the cost, so that we can allocate each cost driver to individual product.
Point to be considered when applying the ABC
ABC can help us to provide more accurate information regarding production cost to set a proper price in a competitive market. It helps the management to understand cost and driver, so we will be able to cut the nonvalue added cost and focus on quality improvement only. Management also is able to rank the cost to be reduced if they wish to join a price war with competitors.
- Cos and benefit?: We have to consider between the cost spend in using ABC and compare with benefit received.
- Do we have enough resource?: The resource is very important in the implementation of ABC, we need to have more people observe each activity in cost pool if the system is not working well. If we want to use a system, we need to buy or build inhouse. The finance team plays an important role in this work, so we need to assign the team to lead this project.
- Can we identify the activity and link with a cost?: This is a very important question to be answered. Some productions are very complicated, we only make assumptions over assumptions, and at the end of the day, it will provide similar results to process costing due to our assumption.