Bad Debt Expense and Allowance for Doubtful Account
Bad debt expense is the uncollectable account receivable when the customer is no longer able to pay their outstanding debt due to financial difficulties or even bankruptcy. The business can not avoid this risk of bad debt when they sell on credit. So should we stop selling on credit? Running a business in this modern-day, we cannot avoid the credit sale. Otherwise, we will face a huge loss, especially when the business getting bigger.
The company will realize its expense when the customer declares bankruptcy, which is too late to recognize a loss in the income statement. Moreover, it will hit the bottom line of the company’s financial statement. And it also not reflect with the matching principle of accrual basic.
Somehow, the company estimates the amount of bad debt when the sale is made. Accounts receivable present in the balance sheet is the net amount, which remains after deducting the allowance for the doubtful account. The doubtful account in balance, which records when they estimate the bad debt.
How to calculate bad debt expense
As we have mentioned above, company has two options when recording bad debt expense, which is the direct write-off and allowance method.
Direct write off
The company does not require to estimate the percentage of the uncollectible debt. They just record sales and accounts receivable. When it is clear that any specific invoice or customer can not be paid, accountants will write off the whole amount to bad debt expense. This account will report in the income statement and reduce the net profit of the company.
Direct write off Journal
For example, Company ABC has found that one of the customers declared bankruptcy last month. This customer still owes ABC 2 invoices ( $ 5,000), so accountants have prepared to write off the whole amount.
The journal entries for direct write off should be:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Bad Debt Expense | $ 5,000 | |
| Accounts Receivable | $ 5,000 |
Allowance method
Different from direct write off, the allowance method requires the management to record the bad debt expense by the time sale is made. So how can we come up with the amount? The answer is we use an accounting estimate to get the estimated amount for recording.
This method will prevent the company from overstating the revenue and profit during and show more transparency in its financial statement. But it also depends on how exactly they intend to estimate their provision.
Bad Debt Expense Formula

Percentage of bad debt: is the estimation by management which base on history data, Accounts Receivable Aging report, risk analysis on customers. Usually, management use the actual bad debt in the past to estimate the percentage of bad debt in the future.
Percentage of bad debt = Bad Debt/Total Accounts Receivable
Allowance method Journal Entries
For example, based on the history data, Company XYZ estimates that 2% of their accounts receivable will be uncollectible. On 01 Jan 202X, the company makes selling on the credit of $ 50,000 from many customers.
Let say the next month, and one customer has gone out of business while owing us the balance of $ 1,000.
Bad Debt Expense = $ 50,000 x 3% = $ 1,500
Journal Entry for allowance method:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Bad Debt Expense | $ 1,500 | |
| Allowance for Doubtful | $ 1,500 |
When we know exactly the bad debt, there will be Journal as following:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Allowance for Doubtful | $ 1,500 | |
| Accounts Receivable | $ 1,500 |
Note: we will not post expense unless the balance is greater than our provision (allowance for doubtful).
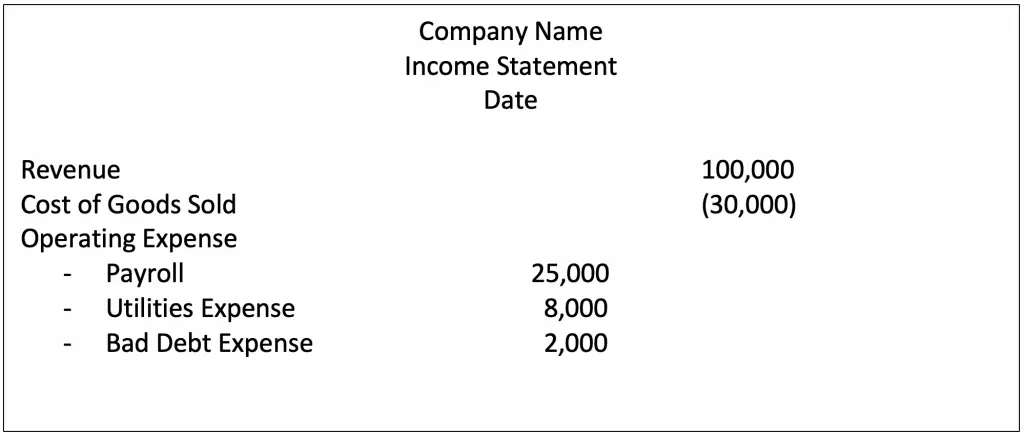
Bad debt expense is reported on the income statement
Bad debt is the expense account, which will show in the operating expense of the income statement. With both methods, the bad debt expense needs to record in the income statement by a different time.
Allowance for doubtful accounts on the Balance Sheet
Allowance for doubtful is the contra asset account with accounts receivable which present in the balance sheet. Most people may confuse this account as the liability, but it is not even it is a negative asset account. It is similar to accumulate depreciation which reduces the fixed balance, but it is not the liability.
